BIOTECHNOLOGY
-
What is a plasmid? small circular DNA molecules
-
A bacteria that appear pink after Gram staining is Gram- and a bacteria that appears purple is Gram+
-
What are the steps of gram staining?
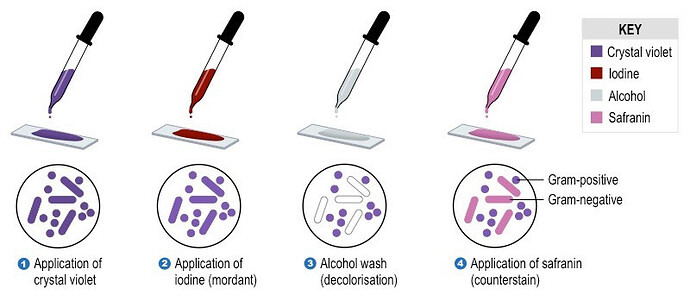
-
What is a plasmid for? Provides the host organism with genetic advantages
-
What are the 6 steps of transgenesis?
-
The first one is to identify the gene of interest
-
Use of restriction enzymes to produce sticky ends in the plasmid
-
Isolation of the required gene using restriction enzymes
-
Mixing the required gene and the plasmid with ligases
-
Identification of the recombinant plasmid
-
Injection of the plasmid into the host cell
-
What is a ligase for?Ligases are enzymes that can stick together 2 bits of DNA strands
-
What is a recombinant plasmid? The recombinant plasmid is the one that has successfully integrated the gene of interest into its sequence
-
What is the characteristic of the cell wall of a Gram+ bacteria? Thick peptidoglycan layer
-
What is a DNA probe? They are sequences of nucleotides that can help identify complementary sequences because they have a fluorescent dye
-
A bacteria with the following characteristics is Gram + or -?
- thin peptidoglycan layer
- outer membrane present
- lipopolysaccharide present
Answer: Gram -
- Explain the principle of ELISA tests
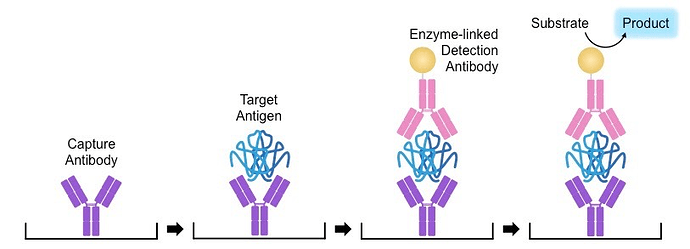
-
The PCR part is a three-step procedure that requires five key elements :
- the DNA samples
- primers that bind to either side of the DNA section: they initiate the PCR reaction
- Nucleotide bases (dNTPs) that are needed to make new DNA strands
- Taq polymerase which adds the new DNA bases
- A buffer that ensures the proper conditions for the reaction
-
How are sticky and blunt ends of DNA obtained? They are obtained by using restriction enzymes
-
Which of the following wells indicate the presence of a disease?
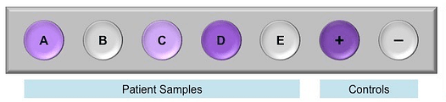
Answer: A, C & D -
How to identify the recombinant plasmid? usage of DNA probes
-
What is gel electrophoresis for? separation technique of DNA, RNA or protein according to their size
-
What is thermal cycling in PCR? the molecules are heated up and cooled repeatedly (20 to 40 times).
-
Explain how gel electrophoresis works?
- electrical field pulls the molecules
- charged samples pulled down the agarose gel
- marker to compare the sizes of the samples
- fluorescent dye to see the strands
This text will be blurred
-
What does ELISA stand for? enzyme-linked immunosorbent essay
-
What is ELISA for? identification method that uses enzyme and color changes