HORMONES
-
Produced by parathyroid. Targets bone and kidney to raise calcite um levels in the blood. Parathyroid hormone
-
Produced by testes. Required in sperm formation and development of genitals. Maintain sexual traits, growth, and development. Androgens
-
Growth hormone (also known as somatotropin) is an anabolic peptide hormone that stimulates growth
-
How does the growth hormone work?
- It acts directly to reduce the formation of adiposefewerls (i.e. fewer nutrients stored as fat)
- It acts indirectly via insulin growth factor (IGF) – produced by the liver – to increase muscle mass and bone size
-
Produced by Hypothalamos. Targets kidneys for water conservation. ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
-
Produced by Hypothalamos. Targets mammary glands and uterus to induce milk movement into secretory ducts and induce uterine contractions during childbirth. OCT (oxytocin)
-
Produced by the Anterior lobe of the Pituitary Gland. Targets the adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of cortisol. ACTH (adrenocorticotropin)
-
Produced by the Anterior lobe of the Pituitary Gland. Targets the thyroid gland to stimulate the release of thyroid hormones. TSH (thyrotropin)
-
Produced by the Anterior lobe of the Pituitary Gland. Targets the ovaries and testes to stimulate estrogen secretion and egg maturation; stimulates sperm production. LH (Luteinizing hormone)
-
Produced by the Anterior lobe of the Pituitary Gland. Targets mammary glands to stimulate and sustain milk production. PRL (prolactin)
-
Produced by the Anterior lobe of the Pituitary Gland. Targets most cells to promote growth and induce protein synthesis, cell division, and metabolism. STH (GH) (Somatotrophin or growth hormone)
-
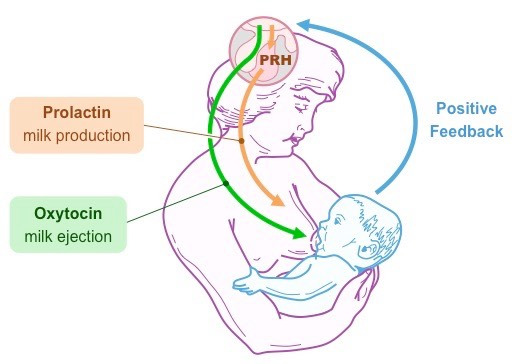
Regarding lactation:
- Prolactin is responsible for the development of the mammary glands and the production of milk
- Oxytocin is responsible for the release of milk from the mammary glands (milk ejection reflex)
-
Describe the hormonal regulation of breastfeeding
-
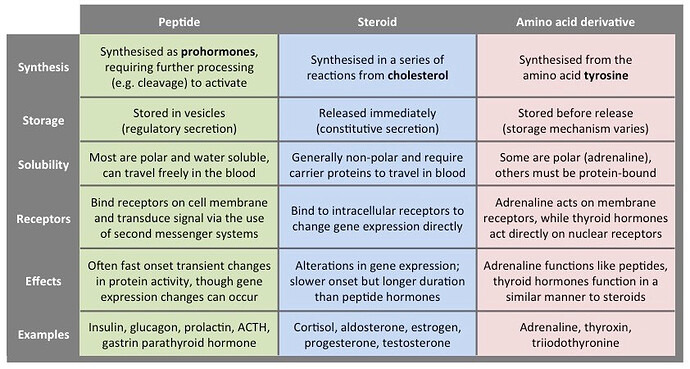
What are the types of hormones? steroid hormones, peptide hormones, and amino acid derivatives
-
What are the differences between the 3 types of hormones?
- synthesis
- storage
- solubility
- receptors
- effects
-
Produced by the adrenal cortex. Target most cells to promote the breakdown of glycogen, fats, and proteins as energy sources; raise the blood level of glucose.Glucocorticoids
-
Produced by the adrenal cortex. Target the kidney to promote sodium reabsorption and help control the salt-water balance. Mineralocorticoids
-
Produced by ovaries. Prepares and maintains uterine lining for pregnancy. Stimulates breast tissues. Progesterone
-
Produced by Pancreatic Islets. Targets liver, muscle, and adipose tissue to promote cellular uptake of glucose and lowers the glucose level in blood. Insulin
-
Produced by Pancreatic Islets. Targets the liver to promote glycogen breakdown and raise glucose levels in the blood. Glucagon
-
Produced by Pancreatic Islets. Targets insulin-secreting cells to inhibit the digestion of nutrients, hence their absorption from the gut. Somatostatin
-
Produced by the thymus. Target T lymphocytes. Thymopoietin and thymosin
-
Produced by the Pineal gland. Target Gonads to influence daily biorhythms and seasonal sexual activity. Melatonin
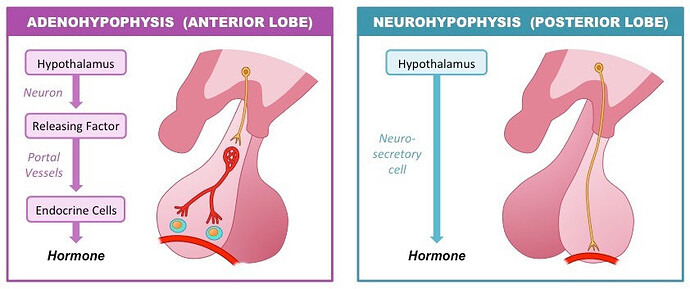
- Describe the differences between anterior and posterior hypophysis
-
Produced by the adrenal medulla. Targets liver, muscle, and adipose tissue to raise the blood level of sugar and fatty acids; increases heart rate and force of contraction. Epinephrine (adrenaline)
-
Produced by the adrenal medulla. Targets smooth muscle of blood vessels to promote constriction or dilation of certain blood vessels thus helping control the flow of blood volume to different regions of the body. Norepinephrine
-
Produced by ovaries. Required for egg maturation and release; prepare the uterine lining for pregnancy and develop genitals, sexual traits, growth, and development. Estrogens
- Pituitary hormones hence control many vital body processes, including:
- Metabolism** (e.g. TSH activates thyroxin)
- Adult Development** (e.g. LH / FSH trigger puberty)
- Reproduction** (e.g. LH / FSH control menstruation)
- Growth** (e.g. growth hormone promotes growth)
- Equilibrium / Homeostasis** (e.g. ADH and water balance)

-
Produced by the thyroid. Target most cells to regulate metabolism. Triiodothyronine and thyroxine
-
Produced by the thyroid. Target bone to lower calcium levels in the blood. Calcitonin