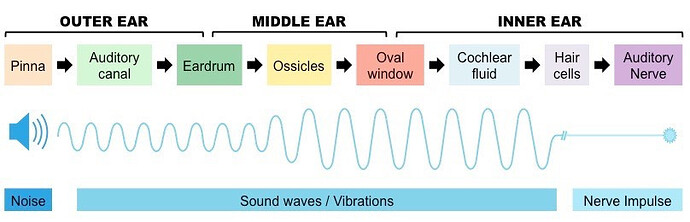
HEARING PHYSIOLOGY AND EAR ANATOMY
-
The external ear is made of the auricle and external auditory canal
-
The eardrum separates the external ear from the middle ear
-
A ruptured eardrum can cause hearing loss
-
The middle ear consists of the ossicles and the eustachian tube
-
The inner ear consists of the cochlea, the vestibule, and the semicircular canals
-
Sounds under 20 Hz are infrasound and above 20 kHz are ultrasounds
-
The cochlea has an oval window: its vibration causes t the displacement of fluid within the cochlea. That movement is detected by hair cells, which triggers the production of nerve impulses that are transmitted to the brain.
-
Describe the trajectory of the sound wave
- How is sounds amplified by the inner ear?
- hydraulic multiplication
- ossicle organization
-
What is hydraulic multiplication? There is an extreme surface difference between the eardrum and the stirrup (21:1). Therefore, the concentrated energy transmitted to the stirrup has a greater pressure.
-
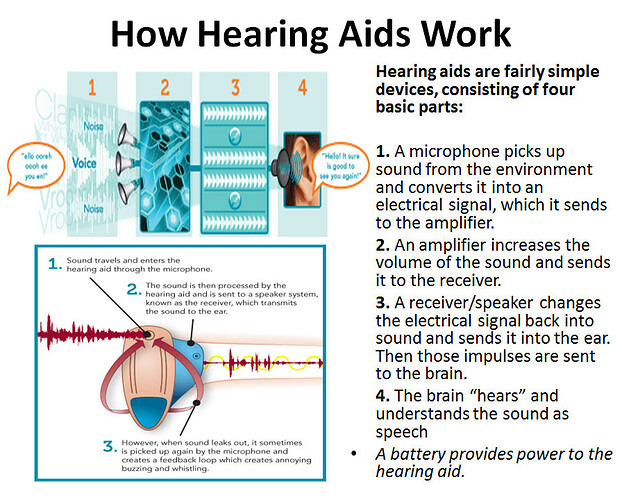
How do hearing aids work?
- A human ear can perceive frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz