CELLULAR RESPIRATION
-
The most common hydrogen carrier is NAD+ which is reduced to form NADH
-
A less common hydrogen carrier is FAD which is reduced to form FADH2
-
The byproduct of glycolysis is 2 pyruvates
-
What is the net gain of glycolysis? 2 ATP + 2 NADH,H+ + 2 pyruvate
-
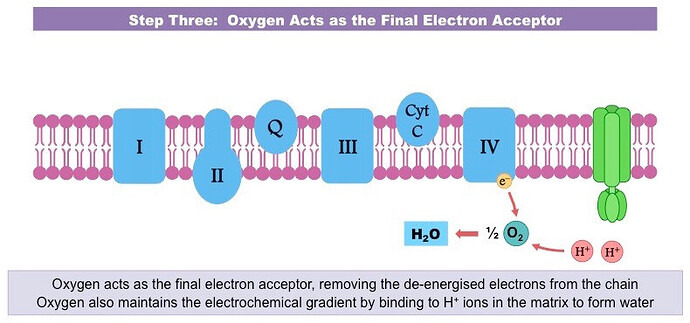
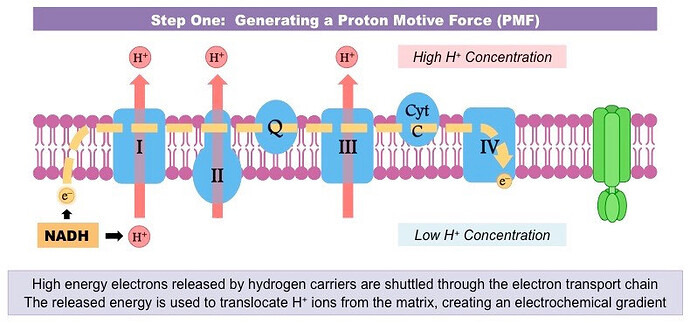
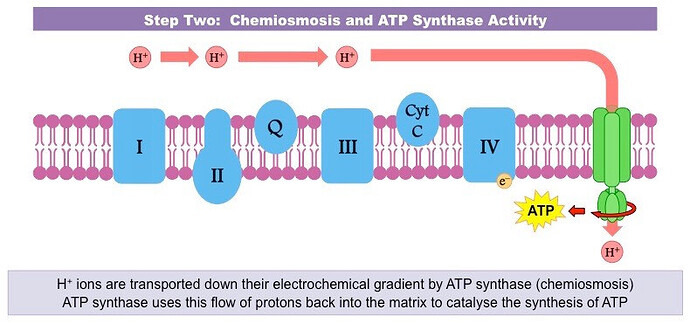
What are the 3 steps of the electron transport chain?
- generating a proton motive
- chemiosmosis and ATP synthase activity
- oxygen acta as the final electron acceptor
-
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol and does not require oxygen
-
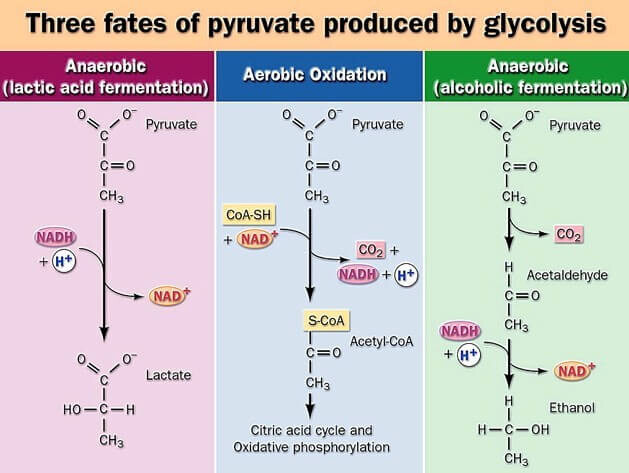
What are the possible fates of pyruvate?
-
Describe alcoholic fermentation: starting molecule, products, a molecule produced
-
Describe aerobic oxidation: starting molecule, products, a molecule produced
-
Aerobic respiration involves 3 types of chemical reactions:
- decarboxylation
- oxidation
- phosphorylation
-
Describe lactic acid fermentation: starting molecule, products, a molecule produced
-
Which reactions are anaerobic?
- lactic acid formation
- alcoholic fermentation
Anwer: both
-
What are link reactions? A stage in cellular respiration that “links” two other stages
-
Pyruvate, through link reactions, produces a 2 carbon compound called acetyl-CoA inside the mitochondria
-
1 glucose, through the Krebs cycle, yeilds 4 CO2, 2ATP, 6NADH, and 2 FADH2
-
The second step of aerobic respiration is the Krebs Cycle
-
In the Krebs cycle, we use Acetyl CoA and a 4C (oxaloacetate) compound to make a 6C compound (Citrate), and the Coenzyme A returns to the link reactions to form another molecule of Acetyl CoA.
-
Decarboxylation occurs in:
- glycolysis
- link reaction
- Krebs cycle
- electron transport chain
Answer: 2 & 3
-
Electron transport chain occurs inside there mitochondria
-
How is proton motive generated?
- Phosphorylation occurs in:
- glycolysis
- Krebs cycle
- electron transport chain
Answer: 1, 2 & 4
- Oxidation occurs in:
- glycolysis
- link reaction
- Krebs cycle
- electron transport chain
Answer: 1, 2 & 3
- Describe the chemiosomis and ATP synthase activity of the electron transport chain
-
1 Glucose molecule will yield about 32-36 molecules of ATP on average, 6CO2, 10xNADH, and 2xFADH2.
-
The electron transport chain is made of 4 complexes: the first and second complexes accept electrons of NADH and FADH2
-
Describe the last step of the electron transport chain