HIV & AIDS
-
How is HIV treated? The treatment for HIV is called anti-retroviral therapy (ART) . However, it cannot cure HIV but only increases the survival rate.
-
HIV is a type of retrovirus that is derived from the simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIV)
-
HIV is a retrovirus, which means that it has RNA instead of DNA and uses the host’s cells to convert it into DNA, thanks to its reverse transcriptase
-
How does ART work? ART stops the multiplication of the virus and reduces its number inside the body. This helps the patient stay healthy.
-
Describe the structure of HIV:
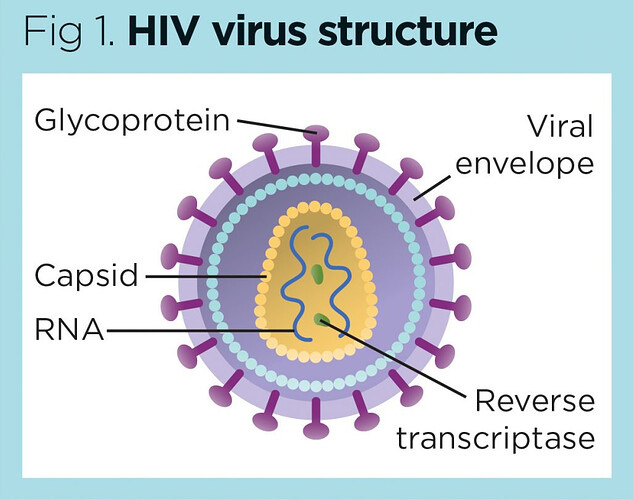
-
HIV targets T cells = CD4 cells
-
How can HIV be transmitted?
Through direct contact with some infected body fluids. This includes:
- blood
- semen
- rectal fluids
- vaginal fluids
- breast milk
- What are the different types of tests?
- Antibody tests: they scan for antibodies in oral fluids and blood
- Antigen/antibody tests: they detect HIV antibodies and antigens in the blood
- Nucleic acid tests: they detect HIV in the blood as well
- HIV multiplication is a 4-step process:
- Binding and entry: HIV fuses with the CD4 cell’s membrane en releases its viral RNA and enzyme inside
- Reverse transcription: the strand of RNA is turned into a double-stranded DNA molecule thanks to the reverse transcriptase
- Replication
- Budding and maturation: the virions are released out of the CD4 cell and can continue the replication process
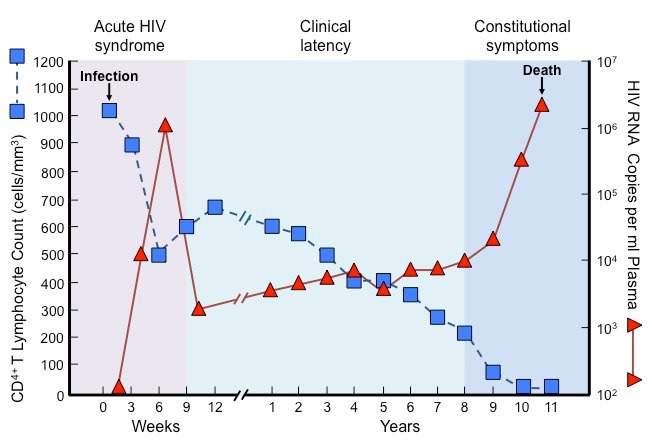
- What are the different infection stages of HIV?