BRAIN ANATOMY AND FUNCTIONS
-
The brain consumes 20% of the body’s energy levels
-
The brain processes sensory information
-
The brain is the integration and coordination system of the body
-
A stimuli generates a motor response
-
Gray matter is made of cell bodies and dendrites
-
The blood-brain barrier is made of endothelial cells
-
The blood brain barrier prevents large molecules to enter the brain
-
True or false: the blood-brain barrier has no impact on treatments (False)
-
White matter is made of axons
-
Myelin serves as an insulator
-
Myelin helps with transmitting information quicker
-
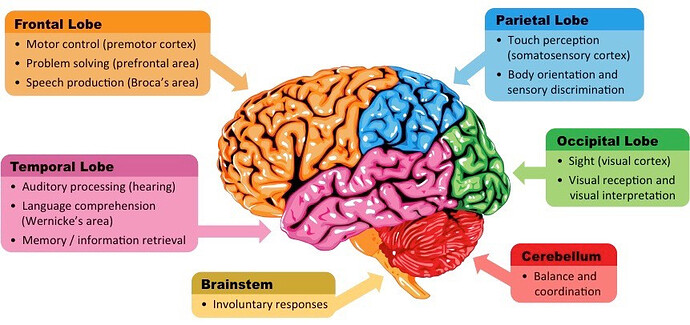
The frontal lobe is for:
- motor control (premotor cortex)
- problem-solving
- speech production (Broca’s area)
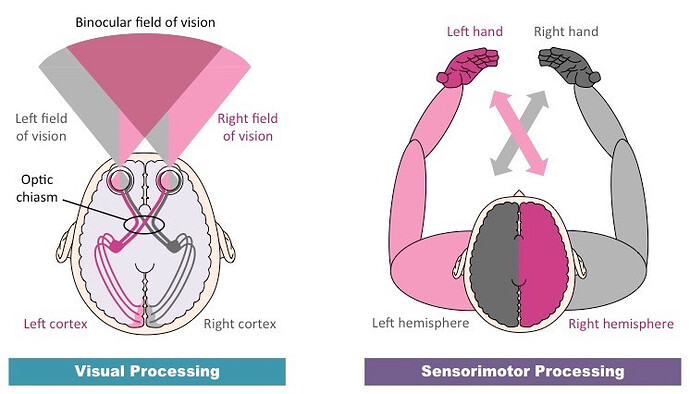
- What is controlateral processing of the brain?
-
What would be the effect of a stroke on the right hemisphere of the brain? Paralysis on the left side of the body
-
There are 6 external brain structures
-
Auditory processing is done by the temporal lobe
-
The visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe
-
The temporal lobe is for:
- hearing
- language comprehension
- memory
-
Broca’s area is for speech production and is located in the frontal lobe
-
Touch perception is permitted by the parietal lobe
-
Wernicke’s area is for language comprehension and is located in the temporal lobe
-
The brainstem is for involuntary responses
-
Balance and coordination is dictated by the cerebellum
-
What is gyrification ? Folding of the brain, for higher density
-
Enlargment of the brain enables cognitive brain capacity
-
The brain stem is composed of:
- the pons
- medulla oblongata
- midbrain
-
The brain stem plays an intermediate role between the brain and the spinal cord
-
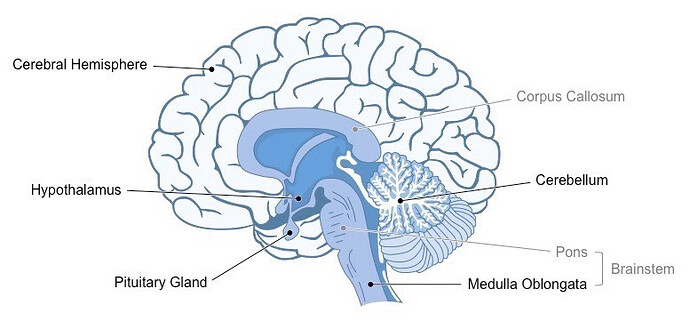
The main internal structures are:
-
The hypothalamus’ main purpose is to maintain homeostasis
-
The hypothalamus plays a role in eating and drinking by stimulating the release of pituitary hormones
-
Glutamate is the neurotransmitter that regulates memory
-
GABA is the calming neurotransmitter
-
The posterior pituitary is also called neurohypophysis and the anterior pituitary is also called adenohypophysis
-
The corpus callosum connects both hemispheres
-
A lesion to the corpus callosum can cause split disorders
-
The nervous system can be divided into the central and peripheral nervous system
-
The central nervous system is composed of the brain and the spinal cord
-
The peripheral nervous system is composed of peripheral nerves = cranial and spinal
-
What is the difference between the sensory division and the motor division of the peripheral nervous system?
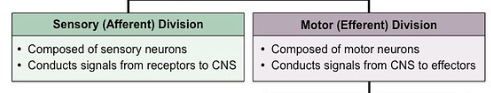
- The motor nervous system can be divided into
autonomic and somatic systems
-
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary responses
-
The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movement
-
Repolarisation is caused by the opening of K+ channels
-
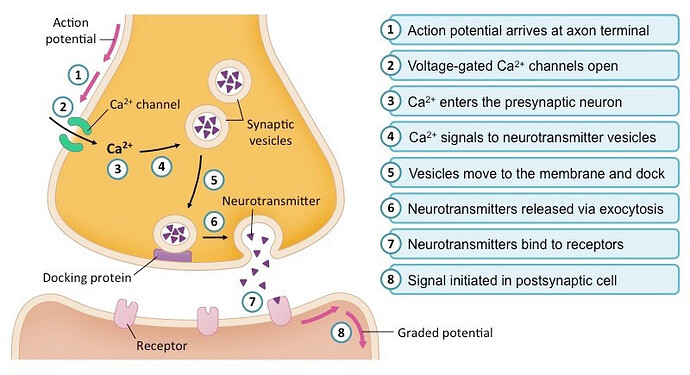
What are the steps of synaptic transfer?
-
The autonomic nervous system can be divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
-
The fight or flight response is mediated by the sympathetic system and the release of adrenaline + (acetylcholine)
-
The feed or breed system is mediated by the parasympathetic system and the release of acetylcholine
-
Cite at least 2 exploration methods of the brain:
- animal experiments
- lesions
- autopsy
- fMRI
-
About the sympathetic nervous system:
- the action of the SNS is quick
- the ganglion is close to the central nervous system
- the pre-ganglionic fibers are short
-
About the parasympathetic nervous system:
-
Its action is a slow response:
-
the pre-ganglionic fibers are long
-
the ganglions are far from the CNS but close to the effector
-
Cite at least 3 hormones that are produced by the pituitary gland:
- LH
- FSH
- oxytocin
- ADH = vasopressin
- hCG
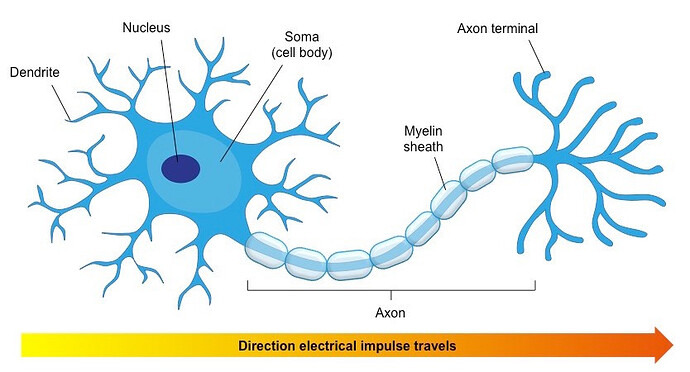
- A neuron has 4 parts: soma + dendrites + axon + terminal buttons
-
The electrical impulse in a neuron goes from cell body to axon terminal
-
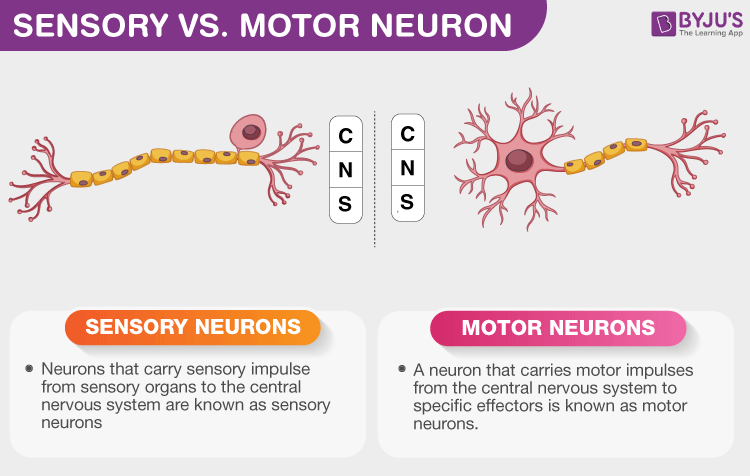
What’s the difference between a sensory and a motor neuron?
-
A resting potential is the difference of electric potential between the 2 sides, outer and inner sides, of the cell membrane
-
The ions responsible for the resting potential are K+, Na+, Ca ++, Cl- and HCO3-.
-
At the resting state, the resting potential is negative (-70 mV )
-
An action potential the inversion of the polarity of the cell membrane
-
An action potential can be divided into depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization
-
Na+ channels open during the depolarisation phase
-
Dopamine is the neurotransmitter for pleasure
-
Serotonin is the neurotransmitter that regulates the mood