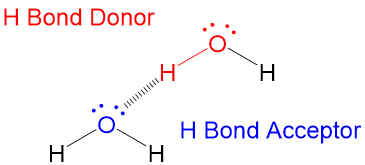
In Hydrogen bonds, the “donor” is the atom giving the lone pair of electrons? or the hydrogen atom?
Electron Pair Donor = Giving e- pair away to another group
Donor is always giving away.
Comes in handy when referring to Lewis Acid & Bases.
Lewis Acids: Accept e- pairs, Electrophiles (NH4+)
Lewis bases: Electron pair donor (OH-), Nucleophiles
Also heavy focus on Redox Reactions.
In hydrogen bonds, the hydrogen atom acts as the “donor,” while the atom with the lone pair of electrons (typically oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) is the “acceptor.”
The hydrogen atom in a hydrogen bond is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom, and Hydrogen atom carries a partial positive charge due to the electronegativity difference between the two atoms. This partial positive charge allows the hydrogen atom to interact with the lone pair of electrons on the acceptor atom, which carries a partial negative charge. This interaction forms a weak electrostatic attraction known as a hydrogen bond.
Think of electron donors as “positive forces” hence the partial positive charge and electron acceptors as “evil forces” hence the negative charge.