In which one of the following reactions is the underlined species acting as an oxidising agent?
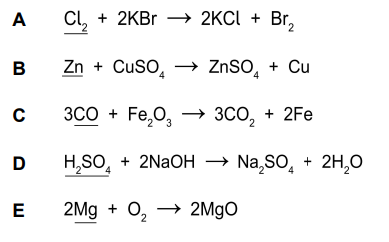
In which one of the following reactions is the underlined species acting as an oxidising agent?
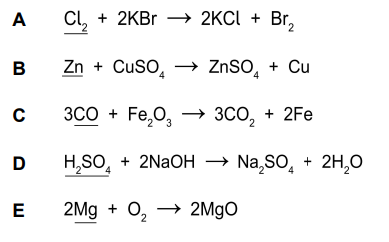
Oxidation/Reduction Recall:
OILRIG
Oxidation is loss of electrons
Reduction is gain of electrons
What is an oxidizing agent?
Causes oxidation in another species (and is reduced itself)
What is a reducing agent?
Causes reduction in another species (it itself is oxidized)
A reduction in oxidation number means that reduction has occur. A rise in oxidation number means that oxidation occurred.
Oxidation Numbers
What are the general rules for assigning an oxidation number?
Summary of most common oxidation numbers
Group 1 (+1), Group 2 (+2), H (+/-1), F (-1), O (-2), Group 7 (-1)
A.
Oxidation Numbers:
Cl_2 : 0
2KBr : K (+1), Br (-1)
2KCl : K (+1), Cl(-1)
Br_2: 0
(Cl_2 reduced, therefore is an oxidizing agent)
B.
Oxidation Numbers:
Zn : 0
CuSO_4 : Cu (+2), S(+6), O(-2)
ZnSO_4 : Zn(+2), S(+6), O(-2)
Cu: 0
(Zn is oxidised and therefore is a reducing agent).
C.
Oxidation Numbers:
CO : C(+2), O(-2)
Fe_2O_3 : Fe (+3), O (-2)
CO_2 : C(+4), O(-2)
Fe: 0
(CO is oxidised and therefore is a reducing agent).
D.
Oxidation Numbers:
H_2SO_4 : H(), S(), O()
NaOH : Na (+1), O (-2), H(+1)
Na_2SO_4: Na(+1), S(+6), O(-2)
H_2O: H(+1), O(-2)
(H_2SO_4 is oxidised and therefore is a reducing agent).
E.
Oxidation Numbers:
Mg : 0
O_2 : 0
MgO : Mg(+2), O(+2)
(Mg is oxidised and therefore is a reducing agent).