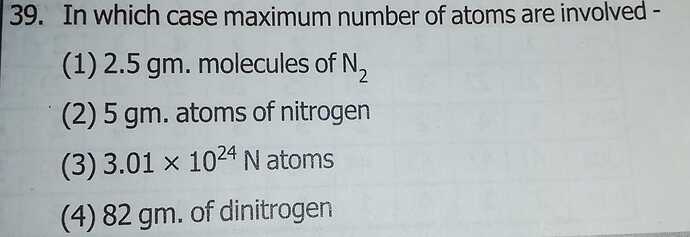Answer - 2
Hi! Could you please include the answers from the textbook?
I have added the answers
unfortunately there are no explanations
Could u please explain them
You can write in a paper and upload too
9 . n=14,6/146=0,1 mol
n of oxygen = (16 * 3 * 2)/16 = 6 mol ( ![]() i don’t understand why n is found with this formula)
i don’t understand why n is found with this formula)
n° of atoms of oxygen= 0,1 * 6 * Na = 0,6 Na
8 . 1 g molecule = 1 mol so:
1 mol of ideal gas = 22,4L
1 mol = 6 * 10²³ molecules = Na
N2 = 14 * 2 = 28g/mol
3 . gaseous oxygen and nitrogen = O2 and N2
if we have 1 kg of mixture we’ll have 1/5 = weight of O2 = 200g
and 4/5 = weight of N2 = 800g
ratio O2 : N2
200g : 800g
100g : 400g
n=100/32 : n=100/7
n° molecules=7 * 100 * Na : n° molecules=32 * 100 * Na
7 : 32 is the simplified ratio
10 .
1- n=4,25/17=0,25
n° atoms = 0,25 * 4 * Na = 1 Na = 6 * 10²³
2- n=4,2/14=0,3
n° atoms = 0,3 Na
each atom has 8 valence electrons so 8 * 0,3 Na = 2,4 Na
3- molar volume at STP=22,4L
n=V/22,4 = 89,6/22,4 = 4
n° molecules = 4 * Na
I hope this helps, let me know if you have any questions, even though this isn’t my strongest subject ![]()
39 . Keep in mind the question is asking for the number of atoms and not molecules!
1 - n=m/M = 2,5/28 = 0,1
n° of atoms = 0,1 * 2 * Na= 1,2 * 10²³
2 - 5/14 = 0,3
n° of atoms = 0,3 * Na = 1,8 * 10²³
3 - 3,0 * 10²⁴ = 30 * 10²³
4 - 82/28 = 3
n° atoms = 3 * 2 *Na = 36 * 10²³ which is the max number of atoms.