The diagram shows the leg muscles of an athlete leaving the starting blocks for a race.
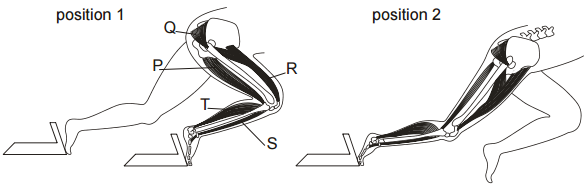
Which muscles contract and which relax to bring about the change from position 1 to position 2?
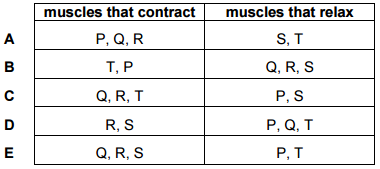
Guys can someone explain why the answer is C
The diagram shows the leg muscles of an athlete leaving the starting blocks for a race.

Which muscles contract and which relax to bring about the change from position 1 to position 2?

Guys can someone explain why the answer is C
Hi!
there are several ways to answer this question:
when a muscle contracts it has a “shorter” and “fatter” appearance, when it relaxes it has a “longer” and “thinner” appearance
From this we can tell P relaxes, R contracts
For the other muscles this is much less obvious to see
think of what movement the muscle is responsible for
To do this imagine a string is attached to the insertion points on the bones, if the string is pulled how would this move your limb?
The calf muscle drawn here is a “string” tied from the top of your tibia and to your tarsal bones, when you pull the string your foot will be pulled back and “pointed”
So T contracts during the movement.
3)If an anterior muscle contracts, its opposite posterior muscle must relax and vice versa
So eliminate all the options that put P and R or S and T in the same column
Hope this helps! also where is this question from?